ICDR stands for Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements. It refers to the rules and regulations laid down by SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) that govern how companies in India can raise money from the public by issuing shares or other securities.
When a company wants to raise funds through the stock market—either by going public with an Initial Public Offer (IPO) or through a Follow-on Public Offer (FPO) or Rights Issue—they must follow the ICDR regulations to ensure transparency and protect investor interests.
What is IPO ( Initial Public Offer)
As per Regulation 2(w) of SEBI ICDR Regulation “initial public offer” means an offer of specified securities by an unlisted issuer (Company) to the public for subscription and includes an offer for sale of specified securities to the public by any existing holders of such specified securities in an unlisted issuer.
What Do you Mean by Specified Securities
As Per Regulation 2(eee) of ICDR 2018 “specified securities” means equity shares and convertible securities.
What is Offer for Sale?
Offer for Sale is a way for existing shareholders of a company (like promoters, investors, or other stakeholders) to sell their shares to the public.
in an OFS, the company doe not get any money — the money goes to the shareholders who are selling their shares.
What is FPO?
As Per Regulation 2(q) of ICDR 2018 “further public offer” means an offer of specified securities by a listed issuer to the public for subscription and includes an offer for sale of specified securities to the public by any existing holders of such specified securities in a listed issuer.
What is convertible securities?
As Per Regulation 2(k) of ICDR 2018 “convertible security” means a security which is convertible into or exchangeable with equity shares of the issuer at a later date, with or without the option of the holder of such security and includes convertible debt instrument and convertible preference shares.
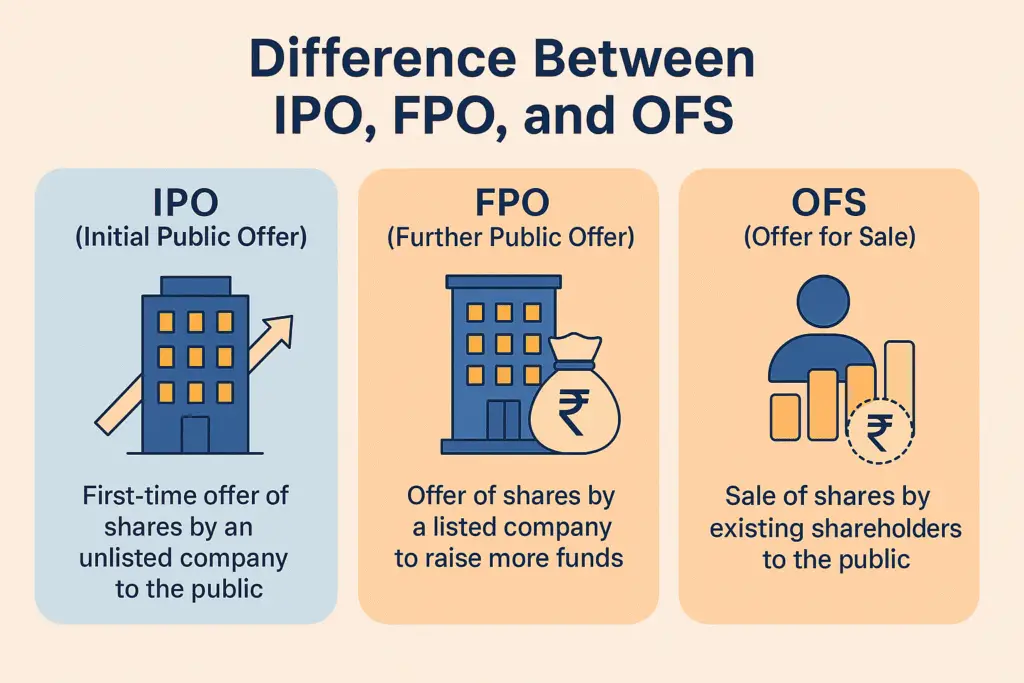
📘 Difference Between IPO, FPO, and OFS
| Particulars | IPO (Initial Public Offer) | FPO (Further Public Offer) | OFS (Offer for Sale) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meaning | First-time offer of shares by an unlisted company to the public | Offer of shares by a listed company to raise more funds | Sale of shares by existing shareholders (like promoters) to the public |
| Issuer | Unlisted Company | Listed Company | Listed Company (shares sold by existing shareholders, not the company itself) |
| Objective | To get listed and raise capital for business | To raise additional capital for expansion, debt repayment, etc. | To allow existing shareholders to exit or reduce their holdings |
| Funds Received By | Company (if fresh issue) / Shareholders (if OFS part included) | Company (for fresh issue) / Shareholders (if OFS included) | Selling Shareholders only |
| SEBI Regulation Reference | Regulation 2(w) of SEBI ICDR Regulations, 2018 | Regulation 2(q) of SEBI ICDR Regulations, 2018 | Covered under SEBI’s framework for OFS – not a capital-raising tool for the company |
| Availability | Open to public – retail, HNIs, QIBs | Open to public – retail, HNIs, QIBs | Usually for QIBs and Non-Retail |
| Listing Status Before the Offer | Unlisted | Already listed | Already listed |
Important Disclaimer
This content is written by Chiman Soni, a CS Executive student and founder of Corporate Laws Hub. The information provided is for educational purposes only and should not be construed as legal or financial advice.
Readers should consult qualified professionals for specific legal or financial queries.
Content Sources
Information compiled from: MCA, ICSI, SEBI, Income Tax Department, GST Portal, IP India, Supreme Court of India, BSE, NSE, and other authoritative sources.
Support Independent Content
Help us continue providing high-quality educational resources by making a donation. Every contribution makes a difference!



